Cortisol Regulation and Endogenous Hypercortisolism
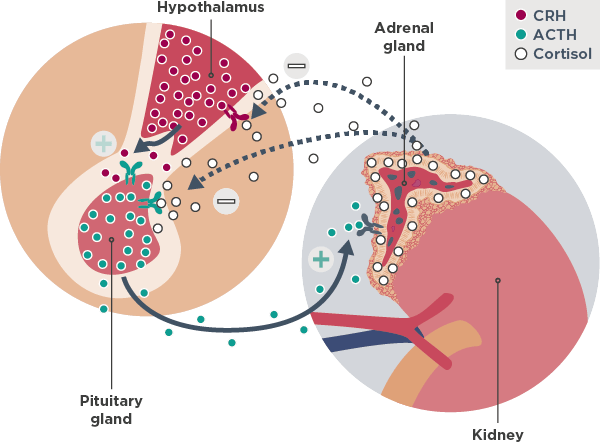
The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis integrates physical, physiological, and psychosocial influences in order to adapt effectively to internal and external factors1
Normal HPA axis functioning includes feedback mechanisms2,3
- Hypothalamus releases corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), which stimulates the pituitary gland
- Pituitary gland subsequently secretes adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), resulting in the activation of the adrenal glands
- Adrenal glands respond by releasing cortisol into the bloodstream
- Hypothalamus and pituitary can reduce the amount of CRH and ACTH, respectively, when there is an adequate amount of cortisol (negative feedback)
Cortisol secretion follows a diurnal rhythm
In healthy, day-working people, cortisol is at its highest level between 6 AM and 8 AM—tapering off during the day and reaching its trough toward midnight.4 This cyclic trough at night is necessary to restore and maintain homeostasis and to avoid development of pathologic conditions.4
Hormone dysregulation outside of the control of normal HPA axis function disrupts feedback influences and can result in hypercortisolism, otherwise known as Cushing syndrome2
Pituitary adenoma (Cushing Disease)
- Secretion of ACTH by a pituitary tumor stimulates the adrenal glands to secrete excess cortisol
Ectopic tumor
- Secretion of ACTH from an ectopic tumor stimulates the adrenal glands to secrete cortisol
Neither pituitary nor ectopic tumors require stimulation by CRH and are usually not sensitive to negative feedback. This leads to unchecked ACTH secretion, high cortisol levels, and loss of diurnal rhythm.
Adrenal adenoma
- Autonomous cortisol secretion independent of ACTH stimulation
- Autonomous cortisol secretion from an adrenal adenoma will reduce ACTH levels
Important Safety Information IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION, INCLUDING BOXED WARNING ON TERMINATION OF PREGNANCY.
BOXED WARNING: TERMINATION OF PREGNANCY
Mifepristone is a potent antagonist of progesterone and cortisol via the progesterone and
glucocorticoid (GR-II) receptors, respectively. The antiprogestational effects will result in the
termination of pregnancy. Pregnancy must therefore be excluded before the initiation of
treatment with Korlym and prevented during treatment and for one month after stopping
treatment by the use of a nonhormonal medically acceptable method of contraception unless
the patient has had a surgical sterilization, in which case no additional contraception is needed.
Pregnancy must also be excluded if treatment is interrupted for more than 14 days in females
of reproductive potential.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Obtain a negative pregnancy test prior to initiating treatment with Korlym in females of
reproductive potential, or if treatment is interrupted for more than 14 days.
Administer once daily orally with a meal. The recommended starting dose is 300 mg once daily.
Renal impairment: Do not exceed 600 mg once daily. Mild-to-moderate hepatic impairment: Do
not exceed 600 mg once daily. Do not use in severe hepatic impairment. Based on clinical
response and tolerability, the dose may be increased in 300-mg increments to a maximum of
1200 mg once daily. Do not exceed 20 mg/kg per day.
Concomitant use of Korlym with a strong CYP3A inhibitor resulted in a 38% increase in mean
plasma concentration of mifepristone. For patients already being treated with a strong CYP3A
inhibitor, start with a Korlym dose of 300 mg per day and titrate to a maximum of 900 mg per
day if clinically indicated. When a strong CYP3A inhibitor is administered to patients already
receiving Korlym, adjust the dose as follows: for patients receiving a daily dose of 600 mg,
reduce dose to 300 mg. For patients receiving a daily dose of 900 mg, reduce dose to 600 mg.
For patients receiving a daily dose of 1200 mg, reduce dose to 900 mg. Titrate if clinically
indicated and do not exceed a Korlym dose of 900 mg in combination with a strong CYP3A
inhibitor.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Pregnancy; patients taking simvastatin or lovastatin and CYP3A substrates with narrow
therapeutic ranges; patients receiving systemic corticosteroids for lifesaving purposes; women
with a history of unexplained vaginal bleeding or endometrial hyperplasia with atypia or
endometrial carcinoma; patients with known hypersensitivity to mifepristone or to any of the
product components.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Adrenal insufficiency: Patients should be closely monitored for signs and symptoms of adrenal
insufficiency.
Hypokalemia: Hypokalemia should be corrected prior to treatment and monitored for during
treatment.
Vaginal bleeding and endometrial changes: Women may experience endometrial thickening or
unexpected vaginal bleeding. Use with caution if the patient also has a hemorrhagic disorder or is
on anticoagulant therapy.
QT interval prolongation: Avoid use with QT interval-prolonging drugs, or in patients with
potassium channel variants resulting in a long QT interval.
Use of strong CYP3A inhibitors: Concomitant use increases mifepristone plasma levels. Adjust
Korlym dose as described in Dosage and Administration. Use only when necessary and do not
exceed a Korlym dose of 900 mg.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions in Cushing’s syndrome (≥20%): nausea, fatigue, headache,
decreased blood potassium, arthralgia, vomiting, peripheral edema, hypertension, dizziness,
decreased appetite, endometrial hypertrophy.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Drugs metabolized by CYP3A: Administer drugs that are metabolized by CYP3A at the lowest
dose when used with Korlym.
CYP3A inhibitors: Caution should be used when Korlym is used with strong CYP3A inhibitors.
Adjust Korlym dose as described in Dosage and Administration. Use only when necessary, and
do not exceed a Korlym dose of 900 mg.
CYP3A inducers: Do not use Korlym with CYP3A inducers.
Drugs metabolized by CYP2C8/2C9: Use the lowest dose of CYP2C8/2C9 substrates when used
with Korlym.
Drugs metabolized by CYP2B6: Use of Korlym should be done with caution with bupropion and
efavirenz.
Hormonal contraceptives: Do not use with Korlym.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Lactation: Mifepristone is present in human milk, however, there are no data on the amount of
mifepristone in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production
during long term use of mifepristone.
Please see accompanying full Prescribing Information and Medication Guide.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Korlym® (mifepristone) is a cortisol receptor blocker indicated to control hyperglycemia
secondary to hypercortisolism in adult patients with endogenous Cushing’s syndrome who have
type 2 diabetes mellitus or glucose intolerance and have failed surgery or are not candidates for
surgery.
Important Limitations of Use
Do not use for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus unrelated to endogenous Cushing’s
syndrome.