BOXED WARNING: TERMINATION OF PREGNANCY
Mifepristone is a potent antagonist of progesterone and cortisol via the progesterone and glucocorticoid (GR-II) receptors, respectively. The antiprogestational effects will result in the termination of pregnancy. Pregnancy must therefore be excluded before the initiation of treatment with Korlym and prevented during treatment and for one month after stopping treatment by the use of a nonhormonal medically acceptable method of contraception unless the patient has had a surgical sterilization, in which case no additional contraception is needed. Pregnancy must also be excluded if treatment is interrupted for more than 14 days in females of reproductive potential.
Contraindications
Pregnancy; patients taking simvastatin or lovastatin and CYP3A substrates with narrow therapeutic ranges; patients receiving systemic corticosteroids for lifesaving purposes; women with a history of unexplained vaginal bleeding or endometrial hyperplasia with atypia or endometrial carcinoma; patients with known hypersensitivity to mifepristone or to any of the product components.
Warnings And Precautions
Adrenal insufficiency: Patients should be closely monitored for signs and symptoms of adrenal insufficiency. See full Prescribing Information for further management instructions.
Hypokalemia: Hypokalemia should be corrected prior to treatment and monitored for during treatment. Measure serum potassium 1-2 weeks after starting or increasing the Korlym dose, and periodically thereafter. Mifepristone-induced hypokalemia should be treated with potassium supplementation based on severity. If hypokalemia persists despite potassium supplementation, consider adding mineralocorticoid antagonists.
Vaginal bleeding and endometrial changes: Women may experience endometrial thickening or unexpected vaginal bleeding. Use with caution if the patient also has a hemorrhagic disorder or is on anticoagulant therapy. Women who experience vaginal bleeding during treatment should be referred to a gynecologist for further evaluation.
QT interval prolongation: Avoid use with QT interval-prolonging drugs, or in patients with potassium channel variants resulting in a long QT interval.
Exacerbation/Deterioration of Conditions Treated with Corticosteroids: For medical conditions in which chronic corticosteroid therapy is lifesaving, Korlym is contraindicated.
Use of strong CYP3A inhibitors: Concomitant use increases mifepristone plasma levels. Use only when necessary and do not exceed a Korlym dose of 900 mg per day.
The labeling contains warnings and precautions for Pneumocystis jiroveci Infection and potential effects of hypercortisolemia. See full Prescribing Information for further management instructions.
Adverse Reactions
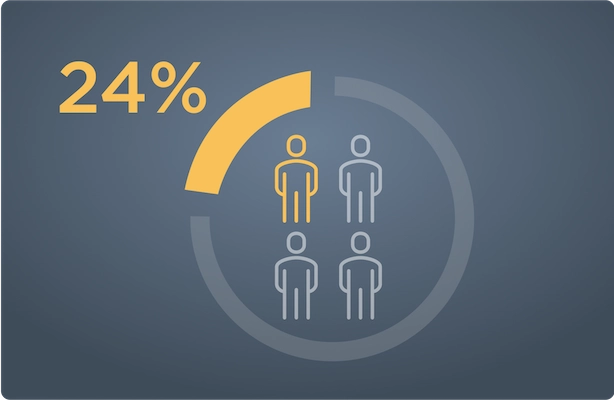
Most common adverse reactions in Cushing’s syndrome (≥20%): nausea, fatigue, headache, decreased blood potassium, arthralgia, vomiting, peripheral edema, hypertension, dizziness, decreased appetite, endometrial hypertrophy.
Drug Interactions
Drugs metabolized by CYP3A: Administer drugs that are metabolized by CYP3A at the lowest dose when used with Korlym.
CYP3A inhibitors: Caution should be used when Korlym is used with strong CYP3A inhibitors. Use only when necessary, and do not exceed a Korlym dose of 900 mg.
CYP3A inducers: Do not use Korlym with CYP3A inducers.
Drugs metabolized by CYP2C8/2C9: Use the lowest dose of CYP2C8/2C9 substrates when used with Korlym.
Drugs metabolized by CYP2B6: Use of Korlym should be done with caution with bupropion and efavirenz.
Hormonal contraceptives: Do not use with Korlym.
Dosage And Administration
Obtain a negative pregnancy test prior to initiating treatment with Korlym in females of reproductive potential, or if treatment is interrupted for more than 14 days.
Administer once daily orally with a meal. The recommended starting dose is 300 mg once daily. Renal impairment: Do not exceed 600 mg once daily. Mild-to-moderate hepatic impairment: Do not exceed 600 mg once daily. Do not use in severe hepatic impairment. Based on clinical response and tolerability, the dose may be increased in 300-mg increments to a maximum of 1200 mg once daily. Do not exceed 20 mg/kg per day.
Concomitant use of Korlym with a strong CYP3A inhibitor resulted in a 38% increase in mean plasma concentration of mifepristone. For patients already being treated with a strong CYP3A inhibitor, start with a Korlym dose of 300 mg per day and titrate to a maximum of 900 mg per day if clinically indicated. When a strong CYP3A inhibitor is administered to patients already receiving Korlym, adjust the dose as follows: for patients receiving a daily dose of 600 mg, reduce dose to 300 mg. For patients receiving a daily dose of 900 mg, reduce dose to 600 mg. For patients receiving a daily dose of 1200 mg, reduce dose to 900 mg. Titrate if clinically indicated and do not exceed a Korlym dose of 900 mg in combination with a strong CYP3A inhibitor.
Use In Specific Populations
Lactation: Mifepristone is present in human milk, however, there are no data on the amount of mifepristone in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production during long term use of mifepristone.
Please see full Prescribing Information and Medication Guide.